
The current Internet is a loose connection of TCP/IP networks organized into a multilevel hierarchy using a wide variety of technologies.Īt the lowest level, computers are connected to each other, and to a router, in a local area network (LAN). Finally, national backbones interconnect in a mesh with other countries, usually with international trunk lines via land, undersea, or satellite.
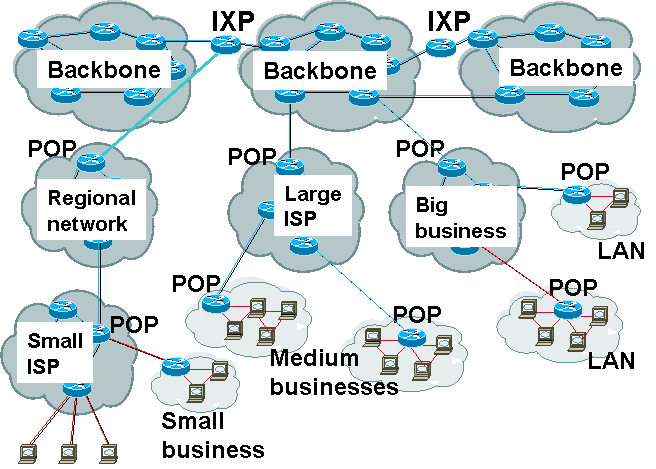
In the United States, these backbones are linked in a small number of interconnection points. A country typically has several backbones linking all of its Internet Service Providers (ISPs). Backbone BasicsĪ backbone is a high-speed wide area network (WAN) connecting lower speed networks. Today, a single government-managed Internet backbone has been transformed into a multitude of different backbones, most of which are private commercial enterprises. National Science Foundation (NSF), linked six supercomputing centers ( University of California- San Diego, National Center for Atmospheric Research, National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois, Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center, Cornell University, and the John von Neumann Supercomputing Center/Princeton) and their associated regional networks in the United States in order to provide supercomputer access to scientists. Thus, the first Internet backbone, called the NSFNET because it was funded by the U.S. government realized that supercomputing was crucial to advances in science, defense, and economic competitiveness but the budget for research was insufficient to provide supercomputers for all scientists who needed them. What happens when you surf the internet.The first Internet backbone was invented to assist in the attempt to share supercomputers.
This allowed the internet to diversify and grow rapidly. May 1995: All commercial use limitations on the internet disappear.July 1992: Delphi became the first national commercial online service to offer internet access.1991: User-friendly internet interface was created.There were commercial restrictions in place at this time because federal funds were being used to run and maintain it. 1986: National Science Foundation funded NSFNET, which is the 56 Kbps backbone of the internet.The invention of these protocols helped to standardize how information was sent and received over the web. 1970s: Transport Control Protocol and Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is established, allowing for internet technology to mature.Late 1960s: Libraries automate and network catalogs independent of ARPANET.October 29, 1969: ARPANET (later renamed internet) created a successful connection between University of California Los Angeles and the Stanford Research Institute.How did we get to the internet we know today? Major breakthroughs Philosophers and authors have conceptualized a shared repository of world knowledge for centuries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
